Robusta coffee has revolutionized the global coffee industry, emerging as a resilient and affordable alternative to Arabica coffee. Its hardiness and adaptability have not only shaped coffee economies worldwide but also influenced coffee culture and trade. This article explores the origins, global impact, and challenges of Robusta coffee, highlighting its pivotal role in reshaping the coffee market. Whether you’re seeking insights into coffee with Robusta beans or the broader international coffee commercial landscape, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable answers.
Table of Contents
The Origins of Robusta Coffee
Introduction of Robusta in Asia
Robusta coffee first gained prominence in Asia during the early 1900s. Dutch colonists introduced Robusta varieties from the Belgian Congo to the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) to combat coffee rust, a disease that had devastated Arabica plantations. By the 1930s, Robusta coffee accounted for over 90% of the East Indies’ coffee output. The variety’s success in Java and Sumatra spurred international trade, with American roasters embracing blends featuring these origins.
The Role of Robusta in African Economies
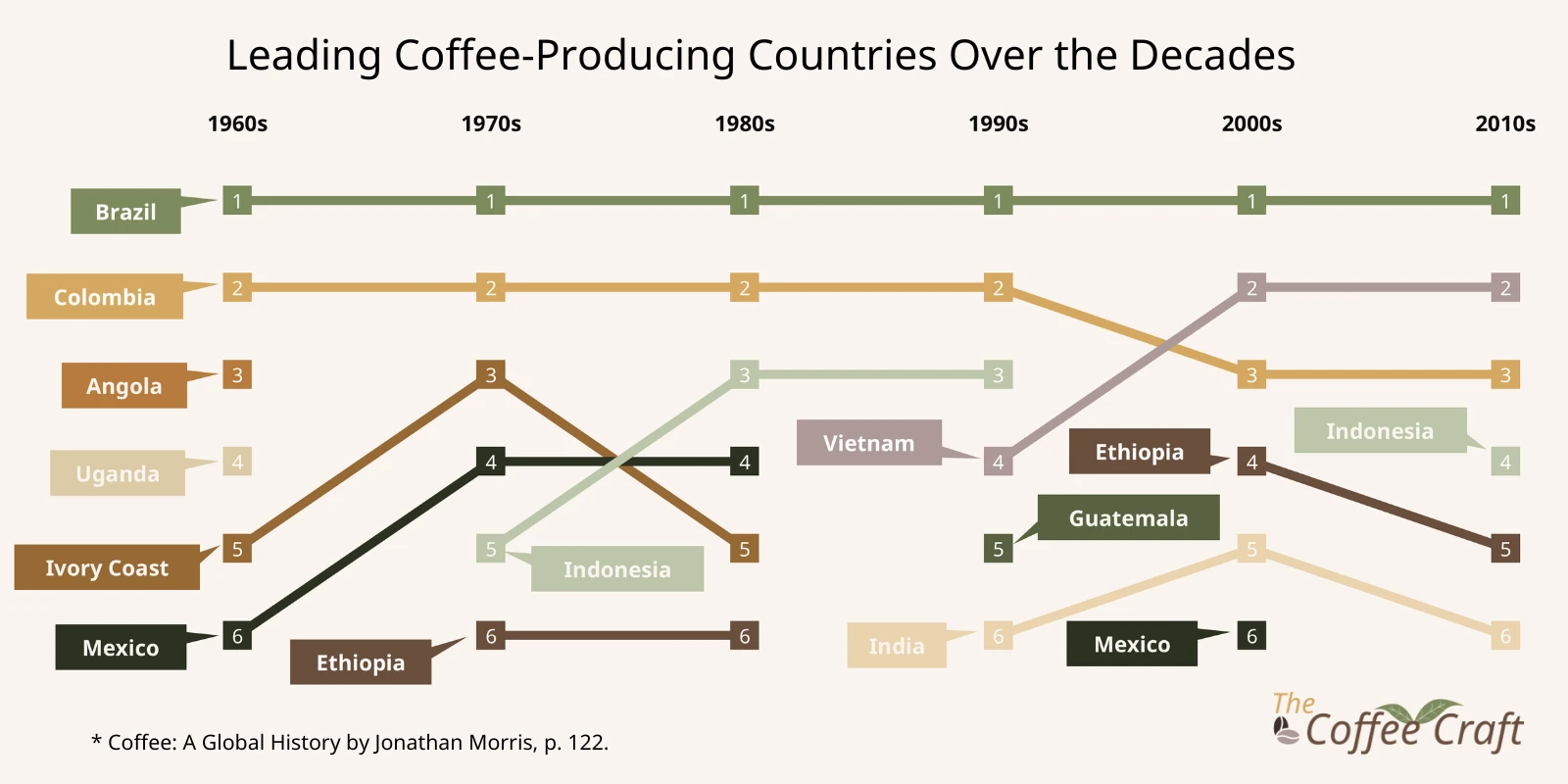
Robusta coffee revitalized Africa’s coffee production after the decline of Mocha. By 1965, Africa’s share of global coffee production had surged from 2% to 23%, with 75% of this output being Robusta. Key contributors included Uganda, Angola, and former French and Belgian colonies. This transformation played a critical role in boosting African economies and reshaping the global coffee market.
Robusta Coffee and Global Trade
Economic Impact on Producing Countries
Robusta coffee has had a profound economic impact on producing countries. The Ivory Coast, for instance, emerged as a leading exporter, increasing production from 16,000 tonnes in 1939 to 279,500 tonnes by 1970. Policies like the Caisse de Stabilisation offered farmers guaranteed prices, encouraging investment and expansion.
However, corruption within similar stabilization systems across Africa has undermined their effectiveness. Price volatility continues to affect smallholder farmers, posing challenges to equitable growth.
Challenges in Governance and Trade
Despite its economic significance, the Robusta coffee trade has faced issues such as corruption and inefficient governance. Small-scale farmers often bear the brunt of price fluctuations, limiting their earnings. Addressing these challenges remains essential for sustainable growth in the trade coffee sector.
Robusta’s Unique Traits and Market Advantage
Resilience and Affordability
Robusta coffee is celebrated for its resilience against diseases and adaptability to various climates. These traits make it a cost-effective choice for producers, enhancing its global accessibility. Its affordability has significantly expanded coffee consumption, particularly in emerging markets.
Consumer Preferences and Blends
Robusta’s bold flavor and high caffeine content make it a popular choice for instant coffee and espresso blends. Its lower cost compared to Arabica has positioned it as a key ingredient in affordable coffee products, catering to mass markets worldwide.
Key Players in Robusta Production
Indonesia’s Coffee Industry
Indonesia’s recovery from wartime disruptions solidified its role as a leading Robusta producer. Government policies aimed at stabilizing production have further enhanced its position in the international coffee commercial landscape.
Uganda’s Focus on Robusta
Uganda’s smallholder farmers have driven Robusta production through innovative practices such as washed processing. Despite challenges during periods of political instability, Uganda remains a significant player in the global Robusta market.
The Global Coffee Market: Robusta’s Role Today
Current Market Trends
Robusta coffee’s share in the global coffee trade continues to grow. Sustainability and ethical sourcing movements are shaping production practices, ensuring better outcomes for farmers and the environment.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, opportunities for improving farmer compensation and governance in the Robusta sector abound. Technological advancements promise to enhance production efficiency and quality, securing Robusta’s place in the future of the global coffee industry.
Conclusion
Robusta coffee has transformed the global coffee industry through its resilience, affordability, and economic significance. From its origins in Asia and Africa to its current role in shaping the coffee market, Robusta’s journey highlights both achievements and challenges. As the industry continues to evolve, Robusta’s influence on global trade and coffee culture remains undeniable. By addressing governance issues and embracing innovation, the Robusta coffee sector can unlock even greater potential in the years to come.
